ADDRESS GEOCODING
by janique savy
19 September 2019
Are addresses important to your company? Is it key to know where your clients are located? Now that you have a list of address data in an Excel spreadsheet ask yourself, now what?
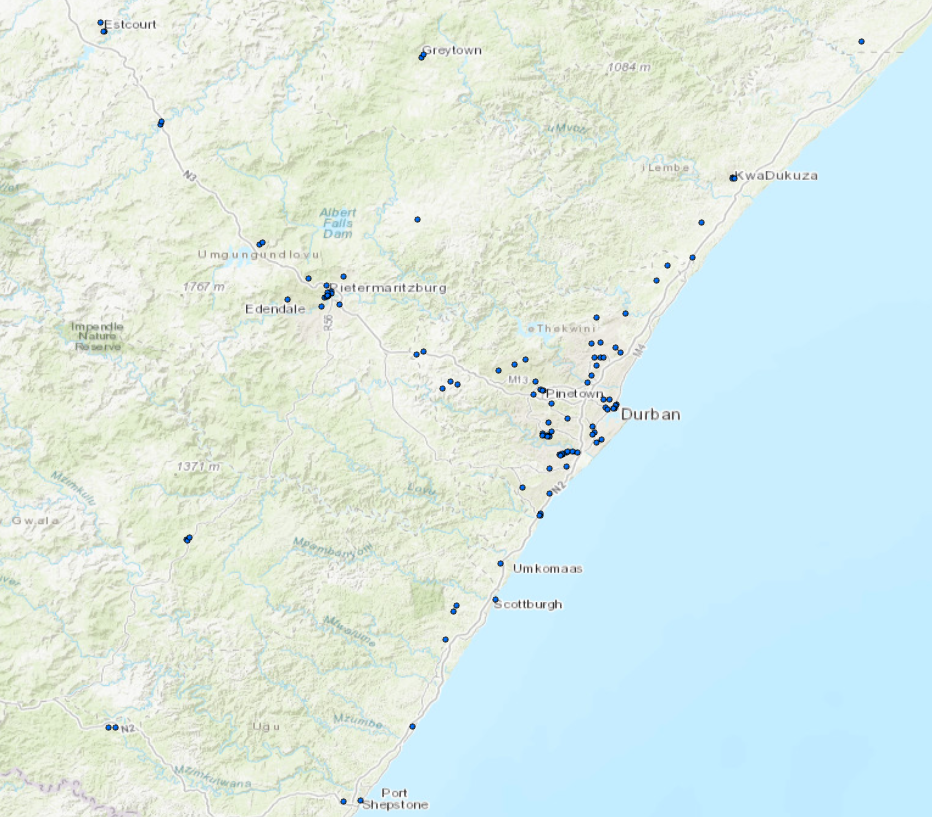
Geocoding is a process that attempts to match the table of addresses to a location, resulting in a point for each address listed in the table. This allows you to visually understand the distribution of your data, opening multiple opportunities. A locator is the main tool for geocoding within ArcGIS and includes reference to various levels of address information, combined with internal logic and search functionality to assist in identifying and locating addresses. This is accomplished by the following process:
Through the processing of routable street datasets, a number of locators can be produced at various reference levels. An address locator is a tool that is used to perform geocoding. These reference levels are the levels at which a given address is matched. The reference levels in order of accuracy are as followed:
Point of Interest: locates a Point of Interest down to the building giving the exact location (Residential and Buildings).

- Point Address: locates an address down to the number giving the exact location of the address (National Address Dictionary).
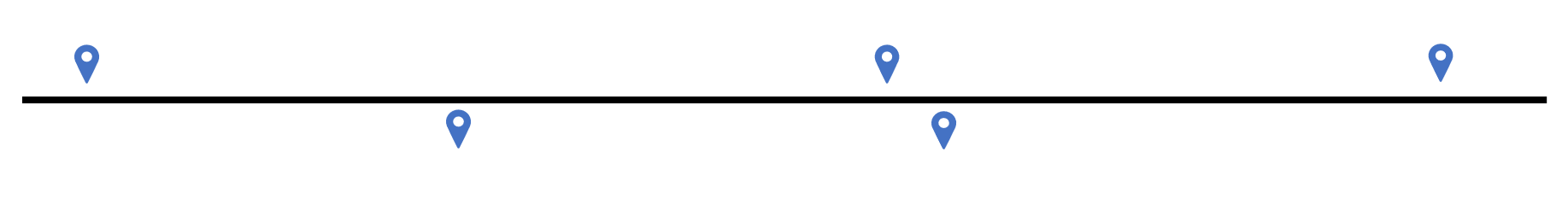
- Street Range Address: interpolates the location of the number on a given street and assumes all land parcels are evenly split. Matches the address down to where the number should be located on a given street. This does not take into account land parcels that may be larger than others such as schools (National Address Range).
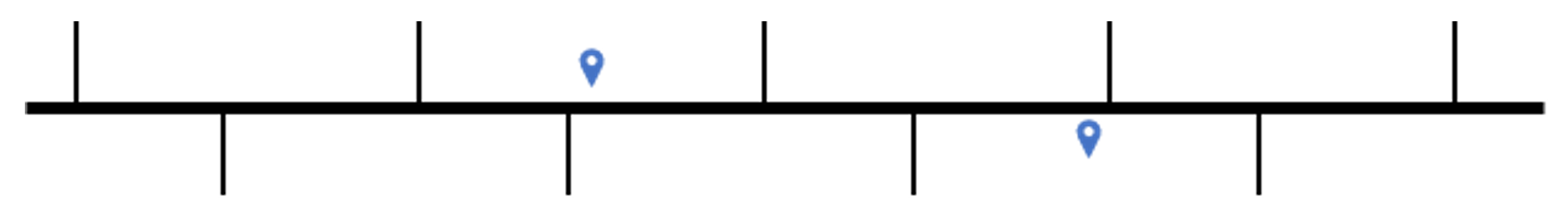
- Street Name: locates the street of the address and positions the point at the centroid of the street in a given suburb.

- Postal Code: locates the postal code of the address and positions the point at the centroid of the postal code.
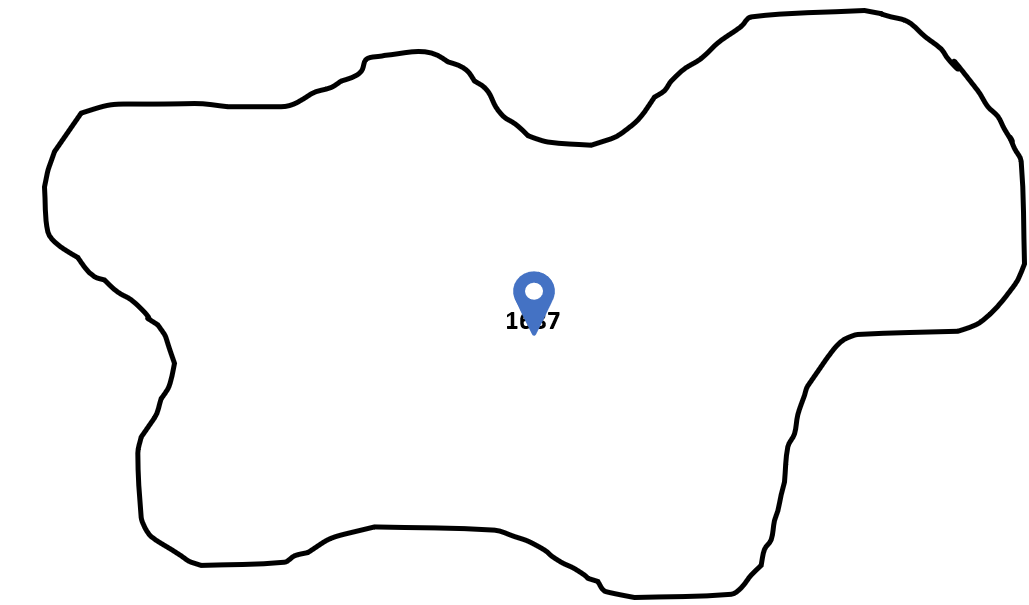
- Locality: locates the suburb of the address and positions the point at the centroid of the suburb.
When geocoding you require a table containing address data and an address locator. In the most ideal situations, the address should contain the following:
- Property Number / Street Number
- Street Name
- Street Suffix
- Locality (Suburb)
- Town
- Postal code
Once the table of addresses are processed using the locators, the results will illustrate which addresses where matched at the various reference level as well as which addresses cannot be matched. The addresses are now represented as points within a map for a more visual perspective of distribution as seen below.